In a groundbreaking archaeological discovery, researchers in China unearthed the tomb of a noblewoman dating back 3,000 years. This remarkable find has captured the attention of the global archaeological community and sparked a flurry of excitement and speculation. As excavations proceeded, researchers uncovered a trove of artifacts and secrets that shed new light on ancient Chinese society and culture, leaving everyone astonished by the revelations.
The tomb, located in a remote region of China, was initially discovered by a team of archaeologists conducting a survey of the area. Its pristine condition and strategic location immediately signaled its significance, prompting further investigation. As researchers carefully began to excavate the site, they were met with a wealth of artifacts and clues that hinted at the identity and status of the tomb’s occupant.

One of the most striking discoveries was the presence of elaborate burial offerings, including finely crafted pottery, jewelry, and ceremonial objects. These artifacts provided valuable insights into the social and economic status of the noblewoman, suggesting that she held a position of prominence within her community. The sheer abundance and quality of the burial goods spoke to the wealth and power wielded by the noblewoman and her family during this period of Chinese history.
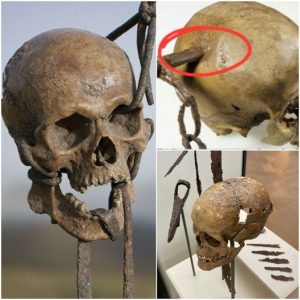
As excavations continued, researchers made another startling discovery: the remains of the noblewoman herself, remarkably well-preserved after millennia of burial. Through meticulous analysis of the skeletal remains and burial context, researchers were able to glean valuable information about the noblewoman’s life and death. Radiocarbon dating and forensic techniques provided insights into her age, health, and possible cause of death, painting a vivid portrait of a bygone era.

But perhaps the most intriguing aspect of the discovery was the presence of inscriptions and hieroglyphics adorning the walls of the tomb. These ancient writings, meticulously carved into the stone, offered tantalizing glimpses into the religious beliefs, customs, and rituals of ancient Chinese society. The inscriptions hinted at the noblewoman’s spiritual journey and provided clues about her role and significance within the community.
As news of the discovery spread, experts and enthusiasts alike were captivated by the revelations emerging from the tomb. The discovery of a 3,000-year-old noblewoman, buried with such pomp and ceremony, offered a rare glimpse into the lives of ancient Chinese elites and the complexities of their society. The artifacts and inscriptions uncovered during the excavation provided invaluable clues for researchers seeking to piece together the puzzle of China’s rich cultural heritage.

Moreover, the discovery of the noblewoman’s tomb underscored the importance of archaeological preservation and exploration in uncovering humanity’s shared history. Each artifact and inscription served as a window into the past, illuminating the lives and legacies of those who came before us. The meticulous work of archaeologists and researchers ensured that these ancient treasures would be preserved for future generations to study and appreciate.

In conclusion, the discovery of the tomb of a 3,000-year-old noblewoman in China stands as a testament to the enduring allure of archaeology and the boundless mysteries of the past. Through careful excavation and analysis, researchers have unlocked a wealth of secrets that offer invaluable insights into ancient Chinese society and culture. As the excavation continues and new discoveries are made, the noblewoman’s tomb will continue to inspire awe and wonder, reminding us of the profound connections that bind us to our shared human heritage.